Blog Updated: July 2024
This one is for you, parents! Yes, it says solar energy for kids in the title, but we’re also hoping you get a moment of reprieve, too. We’ve compiled solar related activities for a wide range of ages, and we also provide a quick primer on the science behind solar energy for kids. Solar energy is not only a fun STEM topic, but it’s also one of the many puzzle pieces that can address the climate crisis we’re facing.
If you’d like advice on how to have a more serious conversation about climate change with your kids, NPR's Life Kit series has a great 20-minute podcast on the subject, “How to Talk to Kids About Climate Change.” It’s a helpful resource for talking to younger and older kids about this complex issue. We also tackled this complex topic in our recent blog post.
Solar Energy for Kids
When explaining complex topics to kids, it's best to stick to the basics and use words they'll understand.
Here's our kid-friendly explanation of solar energy:
Solar panels are a lot like plants. While plants use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into the energy they need to live and grow, solar panels convert sunlight into energy to power your home. But how do solar panels take sunlight and make it into electricity?
Each solar panel is made up of lots of connected solar cells, and these cells are made up of a few layers of materials. There are two layers of silicon (the second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust) that are sandwiched between conductive material. One side of the silicon sandwich has extra electrons (making it negatively charged), and the other has extra holes for electrons to move into (making it positively charged).
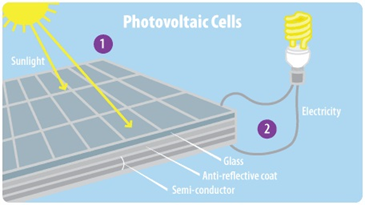
EPA, courtesy
When sunlight hits the silicon, the energy from the sun knocks electrons in the negatively charged side of silicon loose. These electrons then flow through the conductive material to the positively charged side of silicon, creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) flows from your solar cells in your solar panels to what is known as an inverter. Inverters convert DC voltage to alternating current (AC) voltage, which powers your home.
Once they’re done doing their jobs, the electrons that were knocked loose return to their original spots in the silicon, so there’s nothing that gets worn out or used up! This endless loop makes it so solar panels can make clean electricity for decades.
Check out this TED-Ed video for a more visual explanation of how solar panels work:
Solar Energy Activities
That’s enough science and history for now. Let’s inject some fun into these conversations about solar energy with some more hands on games and experiments for kids. There are many solar energy activities for kids, so we’ve split it out into age group.
Elementary School
- Go on an electricity scavenger hunt in your home to find all the places and items that use electricity.
- Play Power Up!, a game from NASA’s Climate Kids program where the goal is to maximize your renewable energy sources to power homes.
- Learn about the power of the sunlight using old crayons and the sun! By following these directions, you can make multi-colored and fun shaped up-cycled crayons.
- What does it look like to live in a cleaner environment? What might renewable energy look like at your house or in your town? Draw us a picture, share it, and tag us @namastesolar. We’d love to see your vision for the future!
Junior High
- Wanna make a light bulb shine using household items? Follow these directions to dive into a super life hack about how to transfer energy using food, or learn more about electricity and the transfer of energy by following along this experiment using little more than magnets and saltwater. We’d love to see your experiments in action! Take a video, share it on social, and tag us @namastesolar.
- Play Offset, a game from NASA’s Climate Kids program with the aim of reducing CO2 output and replanting forests to absorb CO2.
- Create your own word search puzzles or play this crossword puzzle with your kids.
- Take a couple of minutes to test your energy knowledge using the Energy Kids solar IQ test.
High School
- Take a carbon footprint calculator test and find out what your environmental impact is and what you can do to lessen that.
- Dig into the science of electricity and create your own homemade cellphone battery using little more than copper wire and magnets. Create your very own electric motor using some simple household items including a battery, magnet, paper clips, and coil of wire. We’d love to see your experiments in action! Take a video, share it on social, and tag us @namastesolar.
Who’s Who in Solar History
The history of solar is filled with lots of interesting facts and characters. There have been lots of people who played a role to make solar power happen. These historical figures are great for pointing out milestones in solar technology development when explaining solar energy for kids.
- Edmond Becquerel: The story of solar energy began in 1839 when French physicist Becquerel found that when he was experimenting with a cell made of metal electrodes in a conducting solution, the cell produced more electricity when it was exposed to light. This is called the photovoltaic effect.
- Charles Fritts: In 1883, Fritts created the first solar cell by coating selenium with a thin layer of gold. A year later, he installed the first solar panels on a New York City rooftop.
- Albert Einstein: Einstein furthered awareness and acceptance of solar power when, in 1905, he published a paper on the photoelectric effect and how light carries energy. He even went on to win a Nobel Prize for his work on the photoelectric effect.
- Mária Telkes: Telkes was a biophysicist and engineer who immigrated from Hungary to the United States. In 1940, she joined the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Solar Energy Conversation Project and worked on the Dover House project, a house made to be entirely heated by solar. Telkes designed a system based on chemical reactions that would utilize the sun’s energy to heat and cool the house.
- President Jimmy Carter: President Carter had solar panels installed onto the White House roof in the 1970s in order to promote awareness of renewable energy options.
- Hazel O’Leary: From 1993-1997, O’Leary was the first black woman to serve as the U.S. Secretary of Energy. Under the Clinton administration, she was influential in directing federal policy toward prioritizing renewable energy. She also connected energy use with our health and environmental quality and increased financial support for the renewable energy industry.
A Better Future
Unfortunately, whether we like it or not, the climate crisis is here, and kids are paying attention to how we react. Discussing serious topics like global warming and pollution is tough, but the more we arm kids (and ourselves) with knowledge, the more prepared we’ll all be. We believe clean, renewable energy, especially solar, is a better way to power the future, and that by educating the next generation on solar energy we can continue to make our world a better place.
If you're interested in exploring solar power for your home, we'd love to help. You can reach out to our non-commissioned sales team by clicking the button below.
Recommended Reading:
How Solar Energy Works: A Kid Friendly Explanation


